Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 vs. Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009

Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013

Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009
Vue d’ensemble - Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 vs Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009
The Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 and the Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009 are both high-performance supersport motorcycles. While they share some similarities in terms of engine type, bore, stroke, compression ratio, and displacement, they also have distinct differences in various aspects.
In terms of engine power, the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 produces 131 HP, while the Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009 generates slightly more power at 136 HP. However, the torque output of the Kawasaki is 71 Nm, whereas the Suzuki offers a higher torque of 116.7 Nm. This indicates that the Suzuki may have better low-end power and acceleration compared to the Kawasaki.
Both motorcycles have a 4-cylinder engine configuration and utilize an in-line design. The Kawasaki has a displacement of 636 ccm, while the Suzuki has a slightly larger displacement of 999 ccm. This suggests that the Suzuki may have a more powerful and responsive engine overall.

Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013
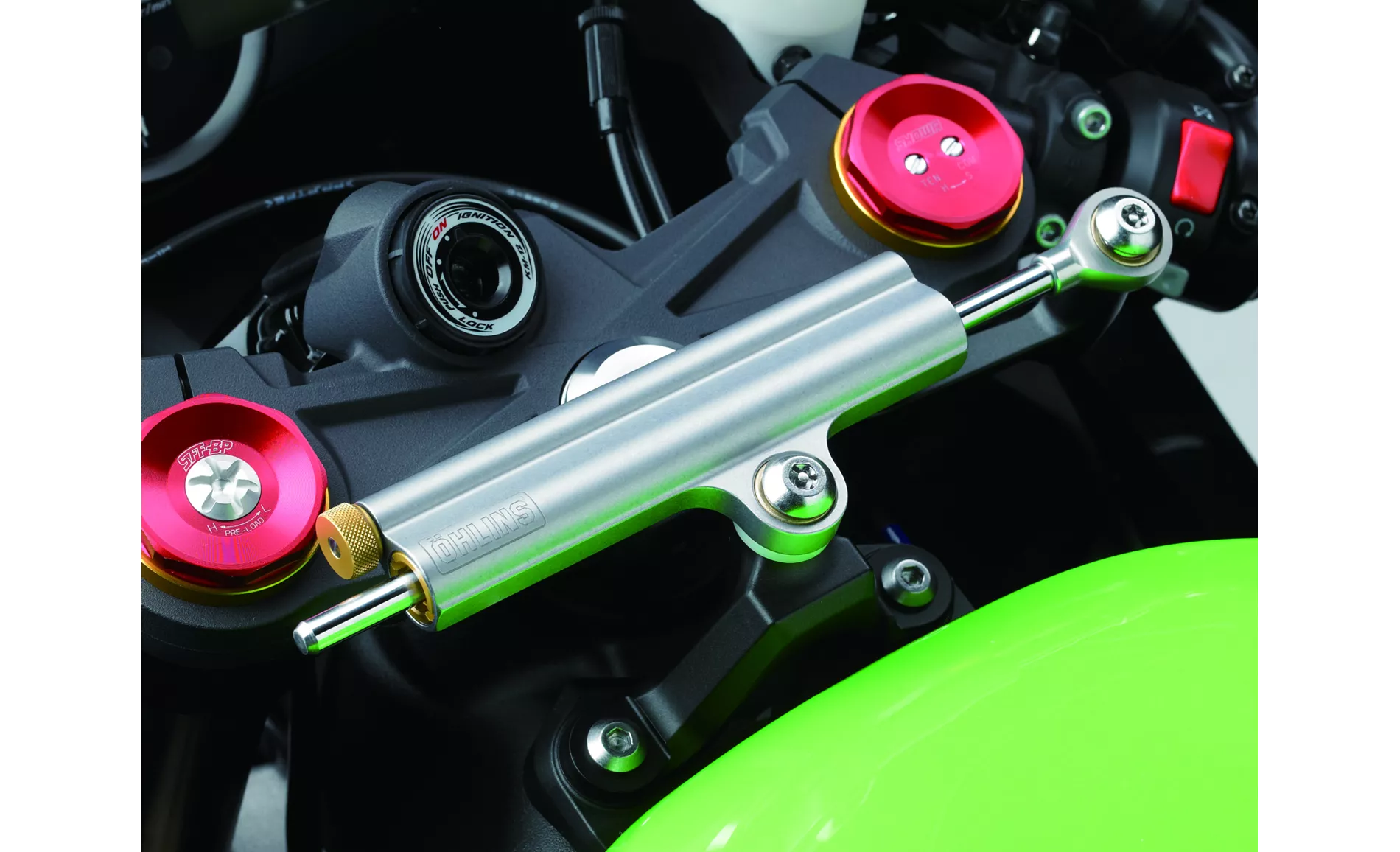
In terms of suspension, both motorcycles offer adjustable compression, preload, and rebound settings for the front and rear suspension. This allows riders to fine-tune the suspension to their preferences and riding style.
Both motorcycles feature an aluminum frame, which provides a good balance between strength and weight. However, the Kawasaki utilizes a twin tube, perimeter, extruded frame type, while the Suzuki uses a twin-spar frame type. The choice of frame design can affect the overall handling and stability of the motorcycle.
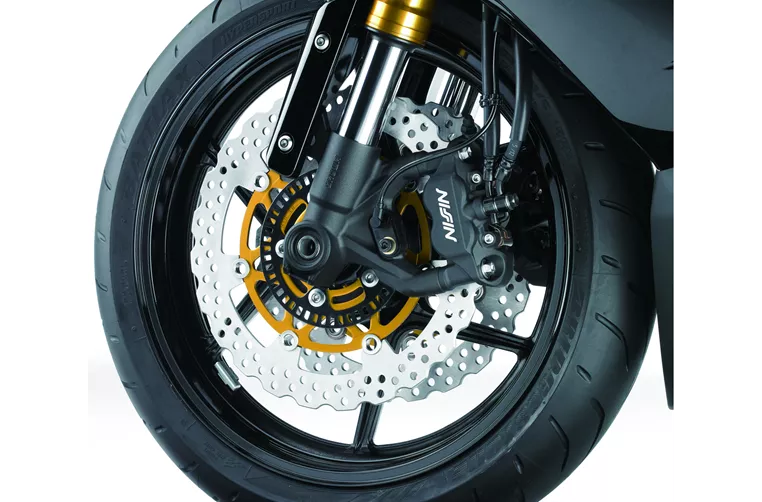
In terms of braking, both motorcycles are equipped with double disk brakes at the front. The Kawasaki utilizes radial, monoblock, petal technology, while the Suzuki uses radial technology. Both braking systems are designed to provide excellent stopping power and control.
In terms of dimensions and weights, there are slight variations between the two motorcycles. The Kawasaki has a front tire width of 120 mm and a rear tire width of 180 mm, while the Suzuki has a slightly wider rear tire width of 190 mm. The wheelbase of the Kawasaki is 1395 mm, while the Suzuki has a slightly longer wheelbase of 1405 mm. The seat height of the Kawasaki is 830 mm, whereas the Suzuki has a slightly lower seat height of 810 mm. The kerb weight of the Kawasaki is 192 kg, while the Suzuki is slightly heavier at 203 kg. Both motorcycles have a fuel tank capacity of around 17 liters.

Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009
When it comes to strengths, the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 is praised for its sharpened geometry, good handling, and uncompromising reliability. On the other hand, the Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009 is commended for its improved geometry, compact engine design, relaxed seating position, system with multiple height adjustments, and anti-hopping clutch.
In terms of weaknesses, the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 is criticized for its high purchase price. On the other hand, the Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009 is noted for its suboptimal accessibility of compression adjustment, weakness in the lower rev range, and not being suitable for beginners.
Overall, both motorcycles offer impressive performance and features, but the Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009 may have a slight edge in terms of power and low-end torque. However, the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 may provide better handling and reliability. Ultimately, the choice between the two would depend on the rider's preferences and priorities.
Caractéristiques techniques Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 par rapport à Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009
Avantages et inconvénients en comparaison
Avantages et inconvénients en comparaison
Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013
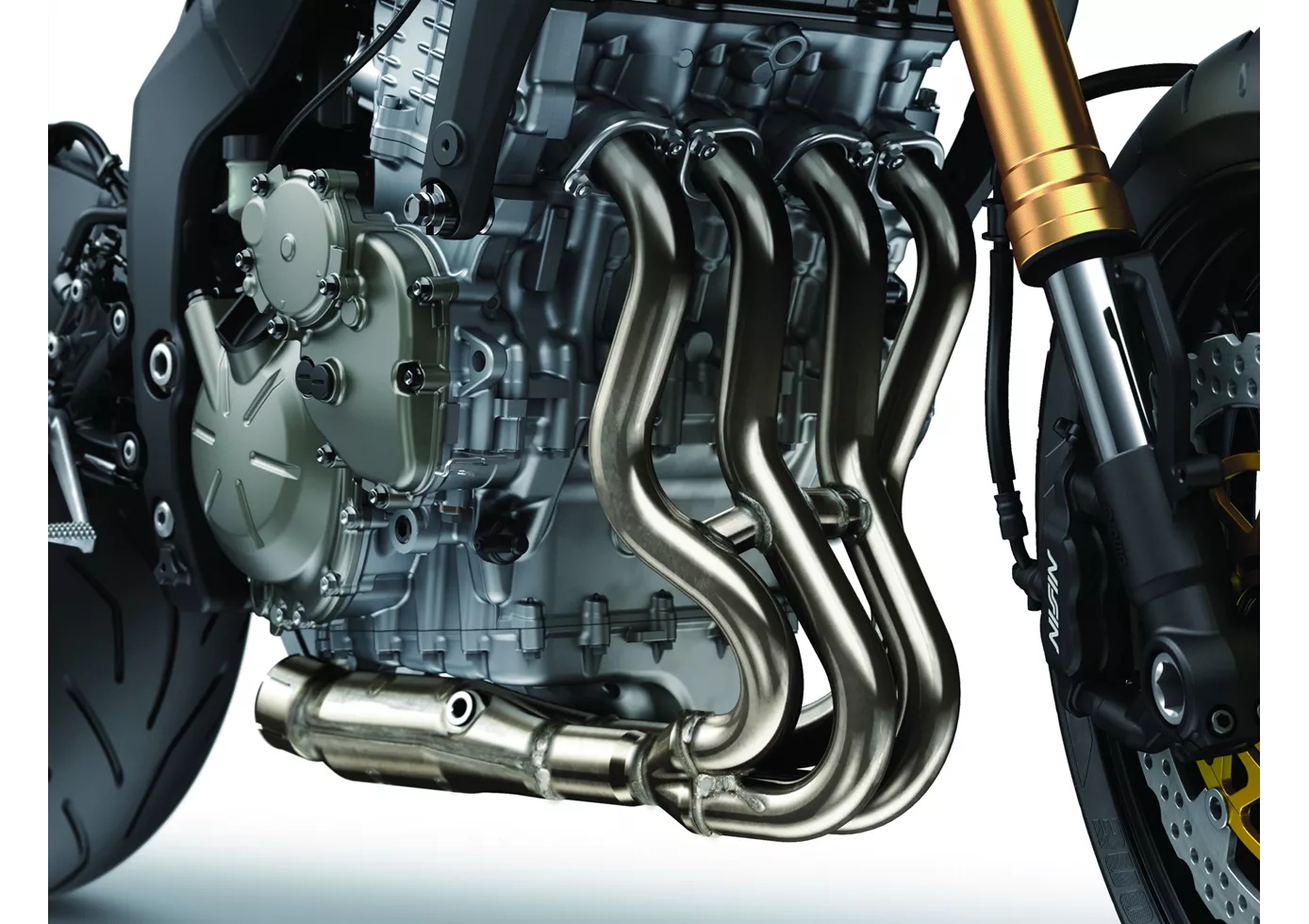
La Kawa convainc par sa bonne maniabilité et sa fiabilité sans compromis. Une moto puissante, mais certainement pas une bonne affaire.
Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009

Malgré une conduite précise et équilibrée et un déploiement de puissance maîtrisé, la GSX-R 1000 reste réservée aux pilotes expérimentés. Suzuki sait qu'un millier doit rester un millier et s'y tient strictement. Espérons qu'elle pourra le faire encore longtemps.
Comparaison des prix Prix moyen du marché Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 vs Suzuki GSX-R 1000
There are a few key differences between a Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 2013 and a Suzuki GSX-R 1000 2009. It takes less time to sell a Suzuki GSX-R 1000 with 64 days compared to 122 days for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636. Since model year 2013 1000PS.de editors have written 7 reviews for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 and 71 reviews for the Suzuki GSX-R 1000 since model year 2005. The first review for the Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R 636 was published on 12/3/2012 and now has more than 20,800 views. This compares to more than 7,100 views for the first review on Suzuki GSX-R 1000 published on 3/3/2004.


















